个人简介
about me:oracle ace pro,optimistic,passionate and harmonious. focus on oracle,mysql and other database programming,peformance tuning,db design, j2ee,linux/aix,architecture tech,etc
文章分类
全部博文(166)
- cbo(54)
- tuning&performan(32)
- concepts&archite(4)
- troubleshooting(5)
- new feature(7)
- sql(50)
- pl/sql(8)
- miscellaneous(3)
- mysql(3)
- 未分配的博文(0)
相关博文
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
分类: oracle
2024-05-08 09:12:57
本文主要讲解,如何建立高效的索引,减少io提高效率,建立组合索引要从哪些方面考虑,从索引访问的路径,访问规则以及索引io计算公式等方面分析。
索引访问过程三步骤:index access,index filter,backward to table(索引访问、索引过滤、回表)
索引访问过程中的选择率ix_sel:也叫effective index selectivity,
是真正用于index access的列的选择率,要遵循leftmost prefix访问规则,ix_sel决定索引访问的cost
索引访问过程中的ix_sel_with_filters:也叫effective table selectivity,
这是访问过程中不遵循leftmost prefix访问规则的列用于索引访问过滤。ix_sel_with_filters不用于计算索引访问的cost
ix_sel和ix_sel_with_filters共同决定了索引扫描返回的行数
backward to table回表过滤也有两种选择率:
1)effective table selectivity:这个就是ix_sel_with_filters,用于计算回表后的costs
2) 回表的condition filter selectivity:回表后的过滤条件,用于计算回表后返回行数
建表语句如下:
统计信息如下:
先了解下索引访问的基础知识:
索引访问过程三步骤:index access,index filter,backward to table(索引访问、索引过滤、回表)
性能好不好,和扫描的数据量(块)有很大关系,结果少,也可能很慢,这主要是实际索引访问扫描的数据量可能很大,
执行计划中没有显示真正扫描的数据量(examined rows),只显示条件返回的rows.
(并发情况下还要检查sql整体指标,比如锁等待)。
要提高索引的使用效率,必须建立高效的索引,让索引access(实际扫描)的数据量少,减少io次数,也即参与索引access的条件选择率要好。
索引获取数据节点:index access,index filter.其中index access是直接访问,比较高效,如果访问的数据量少,则效率高,如果这部分访问的数据量多,
则索引可能不好,然后通过index filter过滤的多,则性能低。
注意执行计划里可能把index filter条件放到了index access里,要注意分辨,主要看index access后的filter条件是不是在access里,在的话,
则主要是index filter条件或者也参与访问但是也会index filter(比如like后通配),这个要看符合不符合索引访问的leftmost prefix规则。
要让返回的数据量尽可能在index access阶段完成,减少index filter过滤的数据量。
对应的index access选择率在10053里是ix_sel,这是真正索引访问选择率,直接决定了扫描的行数,也是计算索引访问cost的主要指标。
索引过滤,也就是索引访问时不能参与access的条件用于filter,对应10053选择率是ix_sel_with_filters,这部分主要和ix_sel结合用于计算索引访问
返回的行数以及回表后的cost.
backward to table:其他额外的非索引条件可能用于回表过滤,如果索引返回行多,回表过滤后很少,则索引可能不好,要考虑重新组织索引顺序。
回表过滤的列选择率*索引返回的rows=回表结果rows。
借用凯发k8官网下载客户端中心官网sql tuning guide index range scan图,可以直观看出索引结构和扫描顺序:
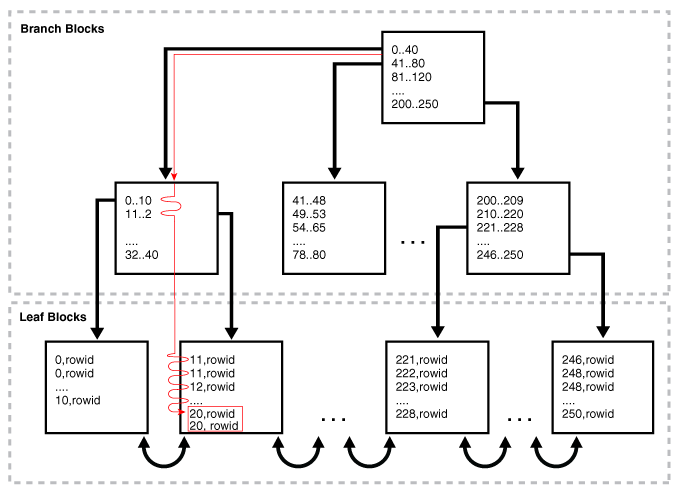
索引访问是从root-->branch--->leaf blocks,一般root到branch的io较少,2-4,索引访问的主要io在轮询leaf blocks上,因为索引访问一般是单块读,
所以io就是cost,可以根据索引访问步骤,很容易推导出轮询leaf blocks的io次数是:blevel leaf_blocks*effective index selectivity(参与索引access的列选择率),
然后回表的io是:index clustering factor * effective table selectivity,index clustering factor是对应相邻索引值在表里的分布情况,越大,说明对应
索引列在表里的分布越离散,这样需要的io就更多。
索引cost/io=
blevel
ceiling(leaf_blocks * effective index selectivity)
ceiling(clustering_factor * effective table selectivity)
从索引访问步骤以及io计算公式可以看出,要想索引效率高,主要effective index selectivity要小,也就是参与索引access的条件选择性要好,以及
clustering_factor要小,effective table selectivity要小,effective table selectivity是索引过滤的选择率,也就是需要回表的行数少,
这样回表次数少,效率高。
总之,索引效率高,主要是io少,索引访问的io少以及回表的io少。
参与index access的索引列要遵循leftmost prefix规则。
leftmost prefix规则如下:
1)索引访问条件要有前导列(skip scan除外)
2)只有前导列是等值的,后续索引列才可能参与access,否则是index filter
3) 如果前导列非等值、不能索引访问的、或前导列不在条件中(断列),则后续列只能index filter
比如前导索引列条件是>,<等,不能索引访问比如like 前通配,<>等
为什么索引访问按照leftmost prefix?很显然,这个和索引结构有关:因为索引是有序排列,这个有序如果是组合索引,
则只有组合索引的前导列值一样,紧跟其后的列才是有序的,因此,前导列条件是等值的,则紧跟其后的列是有序存储,
则可以参与索引访问,如果前导列非等值或不能索引访问,很显然,紧跟其后的列无法确定其访问范围(可能值跨越整个leaf block),
所以只能是在前导列索引访问过程中用于index filter条件,而不是index access条件。
执行计划如下:
按照条件where id = 159 and code between 1000 and 40000查询,可以从执行计划看到,对应的访问条件是:
access("id"=159 and "code">=1000 and "code"<=40000)
符合索引leftmost prefix规则,对应的selectivity是按照id和code组合条件计算:
id和code均无直方图,则
sel(id=159) = 1/num_distinct = density =0.00001
code条件是"code">=1000 and "code"<=40000,先计算sel:
对于范围计算的selectivity = “required range” divided by “total available range”
先查询code列相关信息:
sel的小数位是保留6位,四舍五入:
sel("code">=1000 and "code"<=40000)
= 实际范围/总范围 1/num_distinct 1/num_distinct
=(40000-1000)/(99998-2) 1/63904 1/63904
=.390046898
则条件"id"=159 and "code">=1000 and "code"<=40000的sel是:
0.00001*.390046898=.00000390046898=.000004,小数保留到6位
所以返回的行是:round(.000004*100000)=1,不足1的为1
查询索引信息:
对应总cost=
blevel
ceiling(leaf_blocks * effective index selectivity)
ceiling(clustering_factor * effective table selectivity)
=1
ceiling(290*.000004)
ceiling(341*.000004)
=1 1 1
=3
注意effective index selectivity,指的是索引访问条件的选择率,这里索引访问条件是"id"=159 and "code">=1000 and "code"<=40000,
所以effective index selectivity=sel(id=159)*sel("code">=1000 and "code"<=40000)=0.00001*.390046898=.00000390046898=.000004
对应索引访问的cost=1 ceiling(290*.000004)=2,回表cost=ceiling(clustering_factor * effective table selectivity)=
ceiling(341*.000004)=1,总cost=3
可以从10053里看到:
对应的ix_sel: 0.000004 这个就是effective table selectivity,将.00000390046898四舍五入转为0.000004(小数位保留6位),
ix_sel_with_filters: 0.000004 这个就是effective table selectivity。
索引访问过程三步骤:index access,index filter,backward to table(索引访问、索引过滤、回表)
索引访问过程中的选择率ix_sel:也叫effective index selectivity,
是真正用于index access的列的选择率,要遵循leftmost prefix访问规则,ix_sel决定索引访问的cost
索引访问过程中的ix_sel_with_filters:也叫effective table selectivity,
这是访问过程中不遵循leftmost prefix访问规则的列用于索引访问过滤。ix_sel_with_filters不用于计算索引访问的cost
ix_sel和ix_sel_with_filters共同决定了索引扫描返回的行数
backward to table回表过滤也有两种选择率:
1)effective table selectivity:这个就是ix_sel_with_filters,用于计算回表后的costs
2) 回表的condition filter selectivity:回表后的过滤条件,用于计算回表后返回行数
建表语句如下:
点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
drop table tab1;
-
create table tab1(id number,code number,ext varchar2(100));
-
insert into tab1
-
select mod(level-1,100000)1,
-
ceil(dbms_random.value(0,100000)),
-
'test'||level
-
from dual
-
connect by level <= 100000;
-
-
commit;
-
-
###建立索引id,code
-
create index idx_tab1 on tab1(id,code);
- exec dbms_stats.gather_table_stats(ownname=>user,tabname=>'tab1',method_opt=>'for all columns size 1',no_invalidate=>false);
点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
owner partname nrows blocks avgspc ccnt rowlen ssize anadate
-
---------- ------------------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ---- ------ -------- -------------------
-
dingjun123 100000 370 0 0 20 100000 2024-05-01 16:00:12
-
-
select column_name,low_value,high_value,num_distinct,density,histogram from dba_tab_col_statistics where table_name='tab1';
-
-
column_name low_value high_value num_distinct density histogram
-
------------------------------ -------------------- -------------------- ------------ ---------- ---------------
-
ext 7465737431 746573743939393939 100000 .00001 none
-
code c103 c30a6463 63904 .000015648 none
- id c102 c30b 100000 .00001 none
先了解下索引访问的基础知识:
索引访问过程三步骤:index access,index filter,backward to table(索引访问、索引过滤、回表)
性能好不好,和扫描的数据量(块)有很大关系,结果少,也可能很慢,这主要是实际索引访问扫描的数据量可能很大,
执行计划中没有显示真正扫描的数据量(examined rows),只显示条件返回的rows.
(并发情况下还要检查sql整体指标,比如锁等待)。
要提高索引的使用效率,必须建立高效的索引,让索引access(实际扫描)的数据量少,减少io次数,也即参与索引access的条件选择率要好。
索引获取数据节点:index access,index filter.其中index access是直接访问,比较高效,如果访问的数据量少,则效率高,如果这部分访问的数据量多,
则索引可能不好,然后通过index filter过滤的多,则性能低。
注意执行计划里可能把index filter条件放到了index access里,要注意分辨,主要看index access后的filter条件是不是在access里,在的话,
则主要是index filter条件或者也参与访问但是也会index filter(比如like后通配),这个要看符合不符合索引访问的leftmost prefix规则。
要让返回的数据量尽可能在index access阶段完成,减少index filter过滤的数据量。
对应的index access选择率在10053里是ix_sel,这是真正索引访问选择率,直接决定了扫描的行数,也是计算索引访问cost的主要指标。
索引过滤,也就是索引访问时不能参与access的条件用于filter,对应10053选择率是ix_sel_with_filters,这部分主要和ix_sel结合用于计算索引访问
返回的行数以及回表后的cost.
backward to table:其他额外的非索引条件可能用于回表过滤,如果索引返回行多,回表过滤后很少,则索引可能不好,要考虑重新组织索引顺序。
回表过滤的列选择率*索引返回的rows=回表结果rows。
借用凯发k8官网下载客户端中心官网sql tuning guide index range scan图,可以直观看出索引结构和扫描顺序:

索引访问是从root-->branch--->leaf blocks,一般root到branch的io较少,2-4,索引访问的主要io在轮询leaf blocks上,因为索引访问一般是单块读,
所以io就是cost,可以根据索引访问步骤,很容易推导出轮询leaf blocks的io次数是:blevel leaf_blocks*effective index selectivity(参与索引access的列选择率),
然后回表的io是:index clustering factor * effective table selectivity,index clustering factor是对应相邻索引值在表里的分布情况,越大,说明对应
索引列在表里的分布越离散,这样需要的io就更多。
索引cost/io=
blevel
ceiling(leaf_blocks * effective index selectivity)
ceiling(clustering_factor * effective table selectivity)
从索引访问步骤以及io计算公式可以看出,要想索引效率高,主要effective index selectivity要小,也就是参与索引access的条件选择性要好,以及
clustering_factor要小,effective table selectivity要小,effective table selectivity是索引过滤的选择率,也就是需要回表的行数少,
这样回表次数少,效率高。
总之,索引效率高,主要是io少,索引访问的io少以及回表的io少。
参与index access的索引列要遵循leftmost prefix规则。
leftmost prefix规则如下:
1)索引访问条件要有前导列(skip scan除外)
2)只有前导列是等值的,后续索引列才可能参与access,否则是index filter
3) 如果前导列非等值、不能索引访问的、或前导列不在条件中(断列),则后续列只能index filter
比如前导索引列条件是>,<等,不能索引访问比如like 前通配,<>等
为什么索引访问按照leftmost prefix?很显然,这个和索引结构有关:因为索引是有序排列,这个有序如果是组合索引,
则只有组合索引的前导列值一样,紧跟其后的列才是有序的,因此,前导列条件是等值的,则紧跟其后的列是有序存储,
则可以参与索引访问,如果前导列非等值或不能索引访问,很显然,紧跟其后的列无法确定其访问范围(可能值跨越整个leaf block),
所以只能是在前导列索引访问过程中用于index filter条件,而不是index access条件。
1.前导列是等值的选择率计算
语句如下:点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
select *
- from tab1 where id = 159 and code between 1000 and 40000;
-
1 row selected.
elapsed: 00:00:00.00
点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
execution plan
-
----------------------------------------------------------
-
plan hash value: 2722636538
-
-
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
| id | operation | name | rows | bytes | cost (%cpu)| time |
-
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
| 0 | select statement | | 1 | 20 | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 |
-
| 1 | table access by index rowid| tab1 | 1 | 20 | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 |
-
|* 2 | index range scan | idx_tab1 | 1 | | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
-
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-
predicate information (identified by operation id):
-
---------------------------------------------------
-
-
2 - access("id"=159 and "code">=1000 and "code"<=40000)
-
-
-
statistics
-
----------------------------------------------------------
-
1 recursive calls
-
0 db block gets
-
4 consistent gets
-
0 physical reads
-
0 redo size
-
668 bytes sent via sql*net to client
-
520 bytes received via sql*net from client
-
2 sql*net roundtrips to/from client
-
0 sorts (memory)
-
0 sorts (disk)
- 1 rows processed
access("id"=159 and "code">=1000 and "code"<=40000)
符合索引leftmost prefix规则,对应的selectivity是按照id和code组合条件计算:
id和code均无直方图,则
sel(id=159) = 1/num_distinct = density =0.00001
code条件是"code">=1000 and "code"<=40000,先计算sel:
对于范围计算的selectivity = “required range” divided by “total available range”
先查询code列相关信息:
点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
select column_name,num_distinct,
-
low_value,utl_raw.cast_to_number(low_value) real_low_value,
-
high_value,utl_raw.cast_to_number(high_value) real_high_value
-
from dba_tab_col_statistics
-
where table_name='tab1'
-
and column_name='code';
-
-
column_name num_distinct low_value real_low_value high_value real_high_value
-
------------------------------ ------------ -------------------- -------------- -------------------- ---------------
- code 63904 c103 2 c30a6463 99998
sel("code">=1000 and "code"<=40000)
= 实际范围/总范围 1/num_distinct 1/num_distinct
=(40000-1000)/(99998-2) 1/63904 1/63904
=.390046898
则条件"id"=159 and "code">=1000 and "code"<=40000的sel是:
0.00001*.390046898=.00000390046898=.000004,小数保留到6位
所以返回的行是:round(.000004*100000)=1,不足1的为1
查询索引信息:
点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
select blevel,leaf_blocks,clustering_factor from dba_indexes where index_name='idx_tab1';
-
-
blevel leaf_blocks clustering_factor
-
---------- ----------- -----------------
- 1 290 341
对应总cost=
blevel
ceiling(leaf_blocks * effective index selectivity)
ceiling(clustering_factor * effective table selectivity)
=1
ceiling(290*.000004)
ceiling(341*.000004)
=1 1 1
=3
注意effective index selectivity,指的是索引访问条件的选择率,这里索引访问条件是"id"=159 and "code">=1000 and "code"<=40000,
所以effective index selectivity=sel(id=159)*sel("code">=1000 and "code"<=40000)=0.00001*.390046898=.00000390046898=.000004
对应索引访问的cost=1 ceiling(290*.000004)=2,回表cost=ceiling(clustering_factor * effective table selectivity)=
ceiling(341*.000004)=1,总cost=3
可以从10053里看到:
点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
access path: index (rangescan)
-
index: idx_tab1
-
resc_io: 3.00 resc_cpu: 21754
-
ix_sel: 0.000004 ix_sel_with_filters: 0.000004
-
cost: 3.00 resp: 3.00 degree: 1
-
best:: accesspath: indexrange
-
index: idx_tab1
- cost: 3.00 degree: 1 resp: 3.00 card: 0.39 bytes: 0
ix_sel_with_filters: 0.000004 这个就是effective table selectivity。
给主人留下些什么吧!~~