小公司研发总监,既当司令也当兵!
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
分类: linux
2020-08-18 10:13:56
池化技术
在系统开发过程中,我们经常会用到池化技术。通俗的讲,池化技术就是:把一些资源预先分配好,组织到对象池中,之后的业务使用资源从对象池中获取,使用完后放回到对象池中。这样做带来几个明显的好处:
1),资源重复使用, 减少了资源分配和释放过程中的系统消耗。比如,在io密集型的服务器上,并发处理过程中的子线程或子进程的创建和销毁过程,带来的系统开销将是难以接受的。所以在业务实现上,通常把一些资源预先分配好,如线程池,数据库连接池,redis连接池,http连接池等,来减少系统消耗,提升系统性能。
2),可以对资源的整体使用做限制。这个好理解,相关资源预分配且只在预分配是生成,后续不再动态添加,从而限制了整个系统对资源的使用上限。类似一个令牌桶的功能。
3),池化技术分配对象池,通常会集中分配,这样有效避免了碎片化的问题。线程池
有了上面的池化技术铺垫,理解线程池就很容易了:
1)先启动若干数量的线程,并让这些线程都处于睡眠状态,并以一定的方式组织起来,形成“线程池”;
2)当客户端有一个新请求时,就会从线程池中选取一个线程,并唤醒线程,让它来处理客户端的这个请求;
3)当处理完这个请求后,线程又处于睡眠状态,并且放回到线程池中,等待任务到来调度。
线程池设计
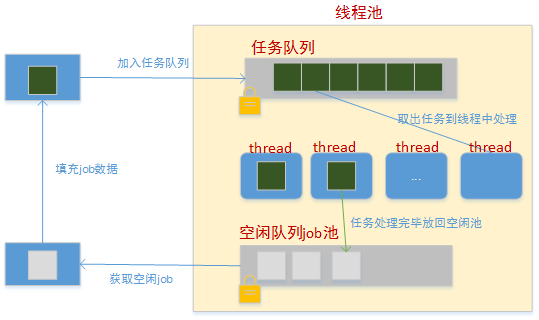
如上图,是基于线程条件变量唤醒的简单线程池模型,主要包括了:任务,任务队列,工作线程几个组件。说明如下:
任务(job)
任务是对一次可执行过的描述,通常包括执行的方法(执行函数)和数据。比如,一个报文接收过程就是一个任务,包括:报文处理函数和报文内容。本例中,对job的定义如下:
点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
typedef struct thread_job {
-
struct list_head list;
-
struct thread_pool* pool;
-
job_process_func jfunc; // 任务执行函数
-
void* data; // 任务数据,由调用者分配,框架释放
- } job_t
任务队列(job_queue)
任务队列缓存着所有待执行的任务,供各个工作线程调度。当工作线程空闲或被唤醒时,会尝试从任务队列中摘取一个任务,然后在线程空间内执行。任务队列用线程互斥锁进行保护。为了方便理解整个任务执行转换的过程,本例中,把空闲任务队列单独出来了。 所以,任务的状态有四种:
1)在空闲对列中等待业务;
2)在业务流程中装配;
3)在工作队列中等待调度;
工作线程
工作线程等待在条件变量上(job_dequeue_valid,新任务需要处理),当新任务到达时,线程被唤醒。线程会尝试从任务队列上获取任务,并执行它;执行完毕后重新等待在条件变量上。如此往复:点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
while (1)
-
{
-
if (thrdp_stopping(pool))
-
{
-
pthread_exit(null);
-
}
-
-
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->qlock));
-
while (list_empty(&pool->job_queue))
-
{
-
// nothing to process, wait until job come in
-
printf("thread<%u> get none job, hangup...\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self() );
-
pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->job_dequeue_valid), &(pool->qlock));
-
-
if (thrdp_stopping(pool))
-
{
-
pthread_exit(null);
-
}
-
-
}
-
job = list_first_entry(&pool->job_queue, struct thread_job, list);
-
list_del(&job->list);
-
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->qlock));
-
job->jfunc(job);
- }
如上代码片段,特别提醒一下,当工作线程从等待条件中被唤醒时,一定要对当前的执行条件再检查,原因是当前线程可能是被“虚假唤醒”。
比如,当前队列是空的,有a,b,c三个工作线程都在等待任务;当一个任务r0到来时,a,b,c三个线程均可能被唤醒;由于任务队列锁的关系,其中只有一个(假如a)取得的实际任务,而b和c均未取得任务,因此b和c称为被“虚假唤醒”。此时,b和c必须对任务获取状态进行再次判断,确保正常获取到任务,方能往下执行调度,否则,应该重新休眠等待任务。
代码实现
附完整代码和测试代码threadpool.h
点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
#ifndef __thread_pool_h__
-
#define __thread_pool_h__
-
#include <linux/types.h>
-
#include <pthread.h>
-
#include <syslog.h>
-
#include <sys/stat.h>
-
#include <unistd.h>
-
#include <stdio.h>
-
#include <stdlib.h>
-
#include <sys/socket.h>
-
#include <sys/types.h>
-
#include <string.h>
-
#include <asm/types.h>
-
#include <linux/netlink.h>
-
#include <linux/socket.h>
-
#include <linux/types.h>
-
#include <sys/socket.h>
-
#include <netinet/in.h>
-
#include <arpa/inet.h>
-
#include <errno.h>
-
#include <unistd.h>
-
-
#include "list.h"
-
-
-
#define thrdp_status_stopping 0x01 // 线程池是否已经关闭
-
-
typedef void (*job_process_func)(void*);
-
-
struct thread_pool
-
{
-
int thread_num; // 线程池中开启线程的个数
-
int max_job_num; // 队列中最大job的个数
-
struct list_head job_queue; // 待处理的job队列
-
struct list_head free_job_queue; // job空闲池
-
-
-
pthread_t *pthreads; //线程池中所有线程的pthread_t
-
pthread_mutex_t qlock; //互斥信号量,保护job_queue
-
pthread_mutex_t fqlock; //互斥信号量,保护free_job_queue
-
pthread_cond_t job_dequeue_valid; // 隊列不為空,需要喚醒線程處理
-
pthread_cond_t job_enqueue_valid; // 隊列沒有滿,可以繼續添加job
-
-
int flags;
-
};
-
-
typedef struct thread_job {
-
struct list_head list;
-
struct thread_pool* pool;
-
job_process_func jfunc; // 任务执行函数
-
void* data; // 任务数据,由调用者分配,框架释放
-
} job_t;
-
-
struct thread_pool* thrdp_new(unsigned int thread_num, unsigned int max_job_num);
-
void thrdp_destroy(struct thread_pool* pool);
-
struct thread_job* thrdp_job_get(struct thread_pool* pool);
-
void thrdp_job_put(struct thread_pool* pool, struct thread_job* job);
-
void thrdp_job_add(struct thread_pool* pool, struct thread_job* job);
-
- #endif
注意,上面引用了list.h,请查看我之前发的用户态list的头文件。
threadpool.c
点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
#include "threadpool.h"
-
-
-
static inline int thrdp_stopping (struct thread_pool* pool)
-
{
-
return pool->flags & thrdp_status_stopping;
-
}
-
-
static void* thrdp_process_func(void* arg)
-
{
-
struct thread_pool* pool = (struct thread_pool*)arg;
-
struct thread_job* job;
-
-
while (1)
-
{
-
if (thrdp_stopping(pool))
-
{
-
pthread_exit(null);
-
}
-
-
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->qlock));
-
while (list_empty(&pool->job_queue))
-
{
-
// nothing to process, wait until job come in
-
printf("thread<%u> get none job, hangup...\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self() );
-
pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->job_dequeue_valid), &(pool->qlock));
-
-
if (thrdp_stopping(pool))
-
{
-
pthread_exit(null);
-
}
-
-
}
-
job = list_first_entry(&pool->job_queue, struct thread_job, list);
-
list_del(&job->list);
-
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->qlock));
-
job->jfunc(job);
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
struct thread_pool* thrdp_new(unsigned int thread_num, unsigned int max_job_num)
-
{
-
struct thread_pool* pool = null;
-
struct thread_job* job;
-
struct thread_job* tmp;
-
int i;
-
-
if(thread_num < 2)
-
{
-
thread_num = 2;
-
}
-
-
if (max_job_num < thread_num)
-
{
-
max_job_num = thread_num;
-
}
-
-
pool = malloc(sizeof(struct thread_pool));
-
if (null == pool)
-
{
-
printf("failed to malloc thread_pool!\n");
-
return null;
-
}
-
memset(pool, 0, sizeof(struct thread_pool) );
-
pool->thread_num = thread_num;
-
pool->max_job_num = max_job_num;
-
-
init_list_head(&pool->job_queue);
-
init_list_head(&pool->free_job_queue);
-
-
if (pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->qlock), null))
-
{
-
printf("failed to init job queue mutex lock!\n");
-
goto error_out;
-
}
-
if (pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->fqlock), null))
-
{
-
printf("failed to init free job queue mutex lock!\n");
-
goto error_out1;
-
}
-
if (pthread_cond_init(&(pool->job_dequeue_valid), null))
-
{
-
printf("failed to init cond job_dequeue_valid!\n");
-
goto error_out2;
-
}
-
if (pthread_cond_init(&(pool->job_enqueue_valid), null))
-
{
-
printf("failed to init cond job_enqueue_valid!\n");
-
goto error_out3;
-
}
-
-
for (i = 0; i < max_job_num; i)
-
{
-
job = (struct thread_job*)malloc(sizeof(struct thread_job));
-
if (null == job)
-
{
-
goto error_out4;
-
}
-
memset(job, 0, sizeof(struct thread_job));
-
list_add(&job->list, &pool->free_job_queue);
-
}
-
-
pool->pthreads = malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * thread_num);
-
if (null == pool->pthreads)
-
{
-
printf("failed to malloc pthreads!\n");
-
goto error_out4;
-
}
-
memset(pool->pthreads, 0, sizeof(pthread_t) * thread_num);
-
-
-
for (i = 0; i < pool->thread_num; i)
-
{
-
pthread_create(&(pool->pthreads[i]), null, thrdp_process_func, (void*)pool);
-
}
-
-
printf("create pool done\n");
-
return pool;
-
-
error_out4:
-
if (!list_empty(&pool->free_job_queue))
-
{
-
list_for_each_entry_safe(job, tmp, &pool->free_job_queue, list)
-
{
-
list_del(&job->list);
-
free(job);
-
}
-
}
-
pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->job_enqueue_valid));
-
error_out3:
-
pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->job_dequeue_valid));
-
error_out2:
-
pthread_mutex_destroy(&(pool->fqlock));
-
error_out1:
-
pthread_mutex_destroy(&(pool->qlock));
-
error_out:
-
free(pool);
-
return null;
-
-
}
-
-
void thrdp_destroy(struct thread_pool* pool)
-
{
-
struct thread_job* job;
-
struct thread_job* tmp;
-
int i;
-
-
if (!pool)
-
{
-
return;
-
}
-
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->qlock));
-
if (thrdp_stopping(pool)) //线程池已经退出了,就直接返回
-
{
-
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->qlock));
-
return;
-
}
-
-
// 設置stop標記,喚醒阻塞的線程,使其退出
-
pool->flags |= thrdp_status_stopping;
-
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->qlock));
-
-
pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->job_dequeue_valid)); //唤醒线程池中正在阻塞的线程
-
pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->job_enqueue_valid)); //唤醒添加任务的threadpool_add_job函数
-
-
for (i = 0; i < pool->thread_num; i)
-
{
-
pthread_join(pool->pthreads[i], null); //等待线程池的所有线程执行完毕
-
}
-
free(pool->pthreads);
-
-
// all threads had done, no one using jobs, just free them
-
if (!list_empty(&pool->job_queue))
-
{
-
list_for_each_entry_safe(job, tmp, &pool->job_queue, list)
-
{
-
list_del(&job->list);
-
free(job);
-
}
-
}
-
-
if (!list_empty(&pool->free_job_queue))
-
{
-
list_for_each_entry_safe(job, tmp, &pool->free_job_queue, list)
-
{
-
list_del(&job->list);
-
free(job);
-
}
-
}
-
-
pthread_mutex_destroy(&(pool->qlock));
-
pthread_mutex_destroy(&(pool->fqlock));
-
pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->job_dequeue_valid));
-
pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->job_enqueue_valid));
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* get a free job
-
* if all jobs busy, wait util someone be free
-
*/
-
struct thread_job* thrdp_job_get(struct thread_pool* pool)
-
{
-
struct thread_job* job;
-
-
if (!pool || thrdp_stopping(pool))
-
{
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->fqlock));
-
while (list_empty(&pool->free_job_queue))
-
{
-
pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->job_enqueue_valid), &(pool->fqlock));
-
if (thrdp_stopping(pool))
-
{
-
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->fqlock));
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
}
-
job = list_first_entry(&pool->free_job_queue, struct thread_job, list);
-
list_del(&job->list);
-
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->fqlock));
-
job->pool = pool;
-
return job;
-
}
-
-
-
/**
-
* put back a used job back to free_job_queue
-
*
-
* this will free the job data which must allocated dynamically
-
*/
-
void thrdp_job_put(struct thread_pool* pool, struct thread_job* job)
-
{
-
int notify = 0;
-
if (!pool || !job )
-
{
-
return;
-
}
-
if (job->data)
-
{
-
free(job->data);
-
job->data = null;
-
}
-
-
memset(job, 0, sizeof(struct thread_job));
-
-
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->fqlock));
-
notify = list_empty(&pool->free_job_queue);
-
list_add_tail(&job->list, &pool->free_job_queue);
-
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->fqlock));
-
-
if (notify)
-
{
-
printf("put back %p to free queue, notify wait jos tasks\n", job);
-
pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->job_enqueue_valid));
-
}
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* add a job to thread-pool for schedule
-
*/
-
void thrdp_job_add(struct thread_pool* pool, struct thread_job* job)
-
{
-
int notify = 0;
-
-
if (!pool || !job )
-
{
-
return;
-
}
-
-
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->qlock));
-
notify = list_empty(&pool->job_queue);
-
list_add_tail(&job->list, &pool->job_queue);
-
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->qlock));
-
-
if (notify)
-
{
-
// notify somebody to handle the new job
-
printf("add new job, notify someone to handle it\n");
-
pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->job_dequeue_valid));
-
}
- }
测试文件thrdp_test.c
点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
#include <stdio.h>
-
-
#include <string.h>
-
#include <stdlib.h>
-
#include <syslog.h>
-
#include <sys/socket.h>
-
#include <sys/types.h>
-
#include <signal.h>
-
#include <getopt.h>
-
#include <netinet/in.h>
-
#include <arpa/inet.h>
-
#include <string.h>
-
#include <sys/select.h>
-
#include <sys/un.h>
-
#include <stddef.h>
-
#include <unistd.h>
-
#include <errno.h>
-
#include <sys/stat.h>
-
#include <fcntl.h>
-
#include <sys/wait.h>
-
#include <unistd.h>
-
#include <uuid/uuid.h>
-
#include <sys/time.h>
-
-
#include "threadpool.h"
-
-
#define srv_port 9966
-
#define udp_pkg_max_len 4096
-
-
struct pkg_desc
-
{
-
int srvfd;
-
struct sockaddr_in cliaddr;
-
char data[udp_pkg_max_len];
-
};
-
-
-
void pkg_process(void* job)
-
{
-
struct thread_job* pjob = (struct thread_job*) job;
-
struct pkg_desc* ppkg = (struct pkg_desc*) pjob->data;
-
-
printf("************* process in %u ******************\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());
-
printf("content:: %s\n", ppkg->data);
-
sendto(ppkg->srvfd, ppkg->data, strlen(ppkg->data), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&ppkg->cliaddr, sizeof(ppkg->cliaddr));
-
thrdp_job_put(pjob->pool, pjob);
-
}
-
-
-
void start_server(void)
-
{
-
struct sockaddr_in srvin, cliin;
-
socklen_t addrlen;
-
int cmd_mgmt_fd;
-
struct thread_pool* pool = null;
-
-
-
cmd_mgmt_fd = socket(af_inet, sock_dgram, 0);
-
if(cmd_mgmt_fd < 0)
-
{
-
printf("start_cmd_mgmt_process socket fd failed.\n");
-
return;
-
}
-
-
memset(&srvin, 0, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in));
-
srvin.sin_family = af_inet;
-
srvin.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
-
srvin.sin_port = htons(srv_port);
-
-
if(bind(cmd_mgmt_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&srvin, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)) < 0)
-
{
-
printf("bind error");
-
}
-
-
-
if ((pool = thrdp_new(2, 8)) == null)
-
{
-
printf("create thread pool error\n");
-
return;
-
}
-
-
while(1)
-
{
-
struct pkg_desc* ppkg = null;
-
struct thread_job* job = thrdp_job_get(pool);
-
int count;
-
-
if (null == job)
-
{
-
printf("get thread process task error\n");
-
return;
-
}
-
ppkg = (struct pkg_desc*) malloc(sizeof(struct pkg_desc));
-
-
if (null == ppkg)
-
{
-
printf("malloc pkg error\n");
-
return;
-
}
-
memset(ppkg, 0, sizeof(struct pkg_desc));
-
-
-
addrlen = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);
-
count = recvfrom(cmd_mgmt_fd, ppkg->data, udp_pkg_max_len, 0, (struct sockaddr*)&ppkg->cliaddr, &addrlen);
-
if(count <= 0)
-
{
-
printf("recvform error\n");
-
continue;
-
}
-
-
ppkg->srvfd = cmd_mgmt_fd;
-
job->data = ppkg;
-
job->jfunc = pkg_process;
-
thrdp_job_add(pool, job);
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
void start_client(int client_id)
-
{
-
struct sockaddr_in srvaddr;
-
struct sockaddr_in peeraddr;
-
int len = sizeof(peeraddr);
-
int fd;
-
char ctnbuf[512] = {0};
-
char rcvbuf[512] = {0};
-
unsigned int i = 0;
-
fd = socket(af_inet, sock_dgram, 0);
-
if(fd < 0)
-
{
-
printf("start_client socket fd failed.\n");
-
return;
-
}
-
-
memset(&srvaddr, 0, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in));
-
srvaddr.sin_family = af_inet;
-
srvaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
-
srvaddr.sin_port = htons(srv_port);
-
-
-
while(1)
-
{
-
-
memset(ctnbuf, 0, 512);
-
sprintf(ctnbuf, "%d say just test:%u", client_id, i);
-
-
sendto(fd, ctnbuf, strlen(ctnbuf), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&srvaddr, sizeof(srvaddr));
-
memset(rcvbuf, 0, 512);
-
len = sizeof(peeraddr);
-
recvfrom(fd, rcvbuf, 512, 0, (struct sockaddr*)&peeraddr, &len);
-
printf("recv content:%s\n", rcvbuf);
-
}
-
}
-
-
int main(int argc, char** argv)
-
{
-
if (argc < 2)
-
{
-
printf("usage : %s [-s/-c] [cid]", argv[0]);
-
return 0;
-
}
-
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "-s"))
-
{
-
start_server();
-
}
-
else
-
{
-
start_client(atoi(argv[2]));
-
}
-
return 0;
-
- }
测试是一个简单的udp回射服务器模型,用线程池的方式做服务端并发。
编译: gcc -g -o thrdp *.c
启动server端: ./thrdp -s
多终端启动client端: ./thrdp -c 100,./thrdp -c 102, ...
运行截图如下