ocp考试资料群:569933648 验证码:ocp ocp 12c 19c考试题库解析与资料群:钉钉群号:35277291
全部博文(486)
- postgresql(55)
- ocp 12c(175)
- ocp(102)
- 未分配的博文(154)
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
- ·
分类: mysql/postgresql
2023-09-14 17:02:32

postgresql从小白到专家,是从入门逐渐能力提升的一个系列教程,内容包括对pg基础的认知、包括安装使用、包括角色权限、包括维护管理、、等内容,希望对热爱pg、学习pg的同学们有帮助,欢迎持续关注cuug pg技术大讲堂。
第29讲:执行计划与成本估算
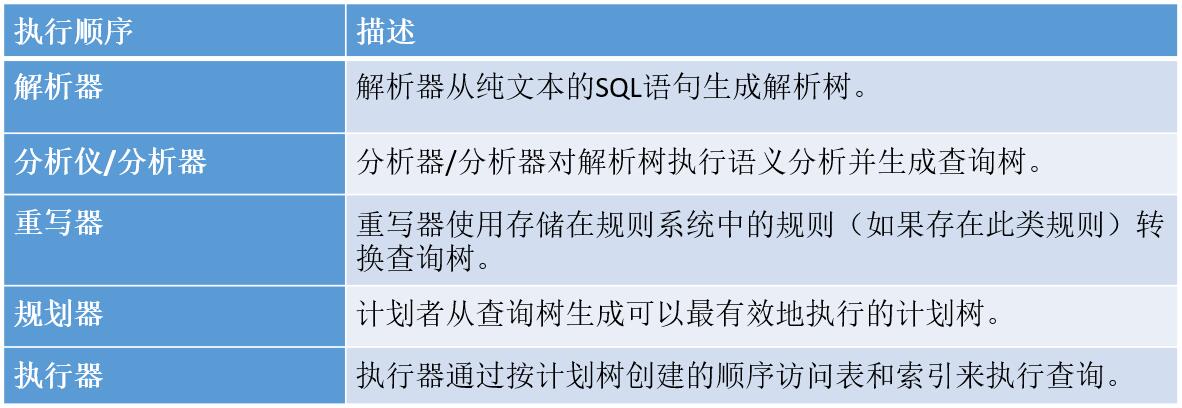
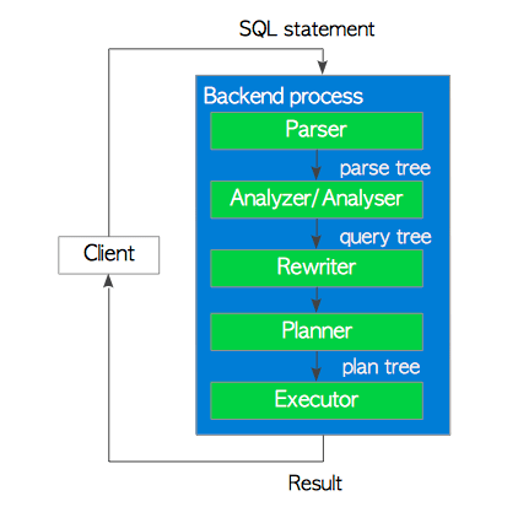
内容1 : postgresql中查询执行流程
内容2 : 全表扫描成本估算
内容3 : 索引扫描成本估算
概述
· sql语句执行五步骤
parser
解析器生成一个解析树,后续子系统可以从纯文本的sql语句中读取该树。
analyzer/analyser
分析器/对解析器生成的解析树运行语义分析,并生成查询树。
rewriter
重写器是实现规则系统的系统,必要时根据pg_rules系统目录中存储的规则转换查询树。
postgresql中的视图是通过规则系统实现的。通过“创建视图”命令定义视图时,将自动生成相应的规则并将其存储在目录中。
假设已经定义了以下视图并且相应的规则存储在pg_rules系统目录中。
create view employees_list
as select e.id, e.name, d.name as department
from employees as e, departments as d
where e.department_id = d.id;
planner and executor
规划器从重写器接收查询树,并生成(查询)计划树,执行者可以{banned}最佳有效地处理该树。
pg_hint_plan插件
postgresql不支持sql中的计划器提示,并且永远不会支持它。如果要在查询中使用提示,需要引用pg_hint_plan扩展插件。
执行计划
· explain显示sql执行计划
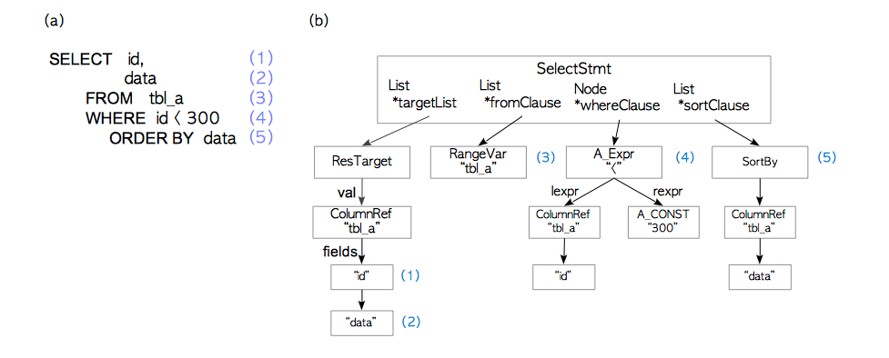
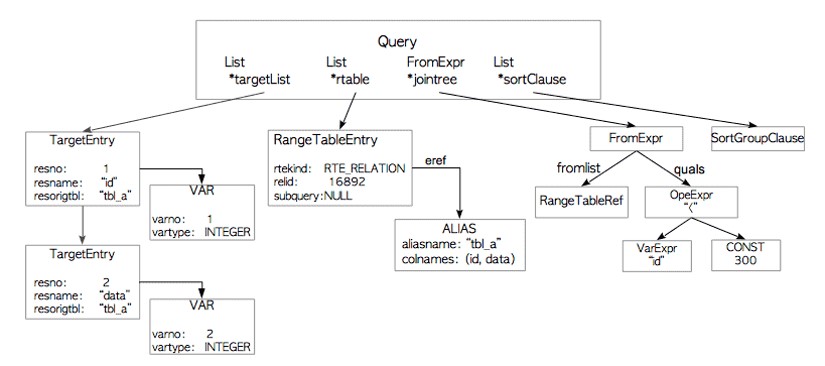
与其他rdbms一样,postgresql中的explan命令显示计划树本身。
例如:
testdb=# explain select * from tbl_a where id < 300 order by data;
query plan
---------------------------------------------------------------
sort (cost=182.34..183.09 rows=300 width=8)
sort key: data
-> seq scan on tbl_a (cost=0.00..170.00 rows=300 width=8)
filter: (id < 300)
(4 rows)
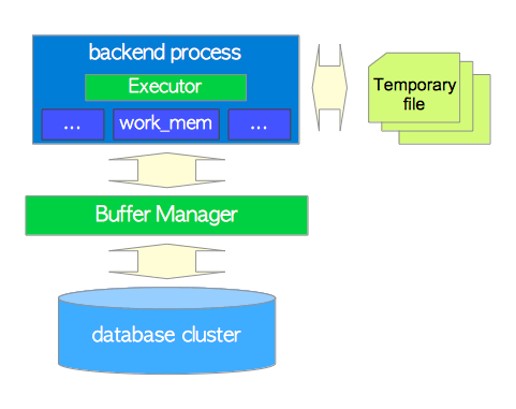
执行器与缓冲区关系
执行器、缓冲区管理器和临时文件之间的关系
单表查询成本估算
· 单表查询中的成本估算
优化基于成本。成本是无量纲值,这些不是绝对的绩效指标,而是比较运营相对绩效的指标。
执行者执行的所有操作都具有相应的成本函数。
三种成本:启动、运行和总计。总成本是启动和运行成本的总和
启动成本是在获取{banned}中国第一个行之前花费的成本。例如,索引扫描节点的启动成本是读取索引页面以访问目标表中的{banned}中国第一个元组的成本。
运行成本是获取所有行的成本。
总成本是启动和运行成本的成本之和。
· 单表查询中的成本估算
explan命令显示每个操作中的启动和总成本。{banned}最佳简单的例子如下所示:
testdb=# explain select * from tbl;
query plan
---------------------------------------------------------
seq scan on tbl (cost=0.00..145.00 rows=10000 width=8)
在第4行中,命令显示有关顺序扫描的信息。在“成本”部分中,有两个值:0.00和145.00。在这种情况下,启动和总成本分别为0.00和145.00。
单表查询成本估算之顺序扫描
· sequential scan成本计算
顺序扫描的成本由cost_seqscan()函数估算。我们将探讨如何估算以下查询的顺序扫描成本。
testdb=# select * from tbl where id < 8000;
在顺序扫描中,启动成本等于0,运行成本由以下等式定义:
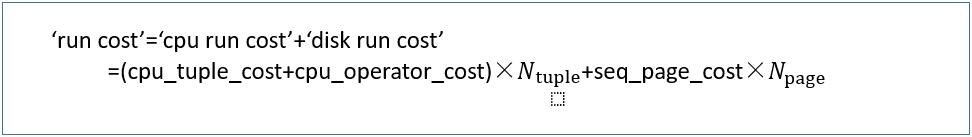
· sequential scan成本计算
查询表的块数(page)和行数(tuple):

根据(1,2)得出
‘run cost’=(0.01 0.0025)×10000 1.0×45=170.0
总成本:
‘total cost’=0.0 170.0=170
· index scan成本估算
计算下面的查询语句通过索引访问成本计算:
testdb=# select id, data from tbl where data < 240;
先查询索引的行数和页数n_(index,tuple) n_(index,page)

· indexscan 成本估算
启动成本计算公式
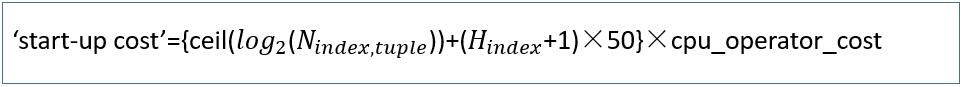
h_index指的是索引的高度
启动成本计算结果:

· indexscan成本估算
运行成本计算公式
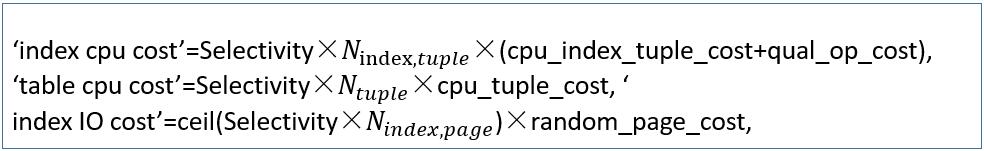
索引扫描的运行成本是表和索引的cpu成本和io(输入/输出)成本之和
‘run cost’=(‘index cpu cost’ ‘table cpu cost’) (‘index io cost’ ‘table io cost’)
前三个成本(即索引cpu成本,表cpu成本和索引io成本)计算公式:
· selectivity
表的每一列的mcv(most common value)作为一对most_common_vals和most_common_freqs的列存储在pg_stats视图中。
most_common_vals({banned}最佳常见的的值)是统计mcvs列表的列。
most_common_freqs({banned}最佳常见值的频率)是统计mcv的频率列。
mydb=# \x
expanded display is on.
mydb=# select most_common_vals, most_common_freqs
from pg_stats
where tablename = 'countries' and attname='continent';
-[ record 1 ]----- ---------------------------------------------------------------------
most_common_vals | {africa,europe,asia,"north america",oceania,"south america"}
most_common_freqs | {0.2746114,0.24352331,0.22797927,0.119170986,0.07253886,0.062176164}
· selectivity
让我们考虑下面的查询,它有一个where子句,“contain=”asia':
testdb=# select * from countries where
continent = 'asia';
select continent, count(*) as "number of countries",
(count(*)/(select count(*) from countries)::real) as "number of countries / all countries"
from countries group by continent order by "number of countries" desc;
continent | number of countries | number of countries / all countries
--------------- --------------------- -------------------------------------
africa | 53 | 0.27461139896373055
europe | 47 | 0.24352331606217617
asia | 44 | 0.22797927461139897
north america | 23 | 0.11917098445595854
oceania | 14 | 0.07253886010362694
south america | 12 | 0.06217616580310881
· selectivity
总结:
与“亚洲”对应的{banned}最佳常见频率值为0.227979。因此,在该估计中使用0.227979作为选择性。
对于列值可选项很高的情况,就不能使用mcv,则使用目标列的直方图界限值来估计成本。
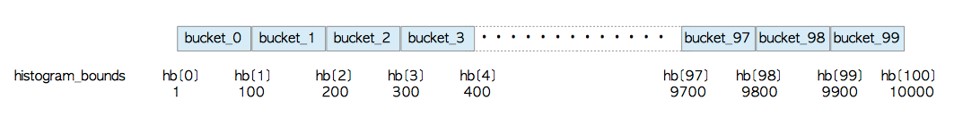
· histogram_bounds
是一个值列表,用于将列的值分成大致相等的总体组
· buckets and histogram_bounds
testdb=# select histogram_bounds
from pg_stats
where tablename = 'tbl' and attname = 'data';
默认情况下,直方图界限被划分为100个桶。上面查询说明了这个例子中的桶和相应的直方图范围。bucket从0开始编号,每个bucket存储(大约)相同数量的元组。直方图界限的值是相应存储桶的界限。例如,直方图上界的第0个值是1,这意味着它是存储在bucket_0中的元组的{banned}最佳小值;第1个值是100,这是存储在bucket_1中的元组的{banned}最佳小值,依此类推。
· selectivity
where data<240计算选择性

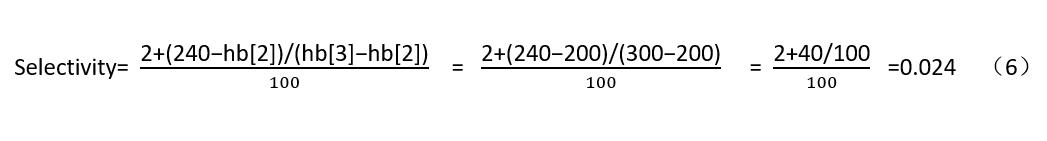
· indexscan成本估算
前三个成本(即索引cpu成本,表cpu成本和索引io成本)计算公式:

根据(1,3,4,6)索引cpu成本、表cpu成本和索引io成本计算结果:
‘index cpu cost’=0.024×10000×(0.005 0.0025)=1.8, (7)
‘table cpu cost’=0.024×10000×0.01=2.4, (8)
‘index io cost’=ceil(0.024×30)×4.0=4.0. (9)
· indexscan成本估算
table io cost计算公式:

· indexscan成本估算
max_io_cost计算公式与结果:

min_io_cost计算公式与结果:

· indexcorrelation
indexcorrelation=1.0 (12)
根据(10,11,12)得出:
‘table io cost’=180.0 〖1.0〗^2×(5.0?180.0)=5.0 (13)
根据(7,8,9,13)得出索引访问总成本:
‘run cost’=(1.8 2.4) (4.0 5.0)=13.2 (14)
· 列的indexcorrelation查询
testdb=# \d tbl_corr
table "public.tbl_corr"
column | type | modifiers
---------- --------- -----------
col | text |
col_asc | integer |
col_desc | integer |
col_rand | integer |
data | text |
indexes:
"tbl_corr_asc_idx" btree (col_asc)
"tbl_corr_desc_idx" btree (col_desc)
"tbl_corr_rand_idx" btree (col_rand)
testdb=# select * from tbl_corr;
col | col_asc | col_desc | col_rand | data
---------- --------- ---------- ---------- ------
tuple_1 | 1 | 12 | 3 |
tuple_2 | 2 | 11 | 8 |
tuple_3 | 3 | 10 | 5 |
tuple_4 | 4 | 9 | 9 |
tuple_5 | 5 | 8 | 7 |
tuple_6 | 6 | 7 | 2 |
tuple_7 | 7 | 6 | 10 |
tuple_8 | 8 | 5 | 11 |
tuple_9 | 9 | 4 | 4 |
tuple_10 | 10 | 3 | 1 |
tuple_11 | 11 | 2 | 12 |
tuple_12 | 12 | 1 | 6 |
(12 rows)
· indexcorrelation与表之间的关系
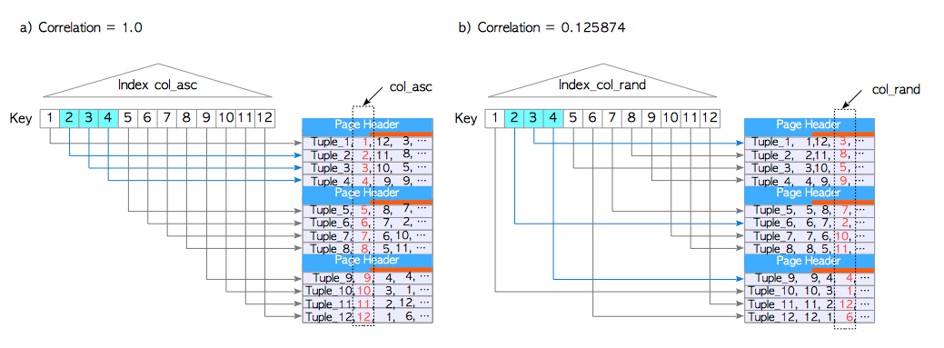
· 列的indexcorrelation查询
testdb=# select tablename,attname, correlation from pg_stats
where tablename = 'tbl_corr';
tablename | attname | correlation
----------- ---------- -------------
tbl_corr | col_asc | 1
tbl_corr | col_desc | -1
tbl_corr | col_rand | 0.125874
· 总成本
根据(5,14),得出通过索引访问表的总代价:
(5)--启动成本
(14)--通过索引访问表的成本
‘total cost’=0.285 13.2=13.485 (15)
testdb=# explain select id, data from tbl where data < 240;
query plan
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
index scan using tbl_data_idx on tbl (cost=0.29..13.49 rows=240 width=8)
index cond: (data < 240)
· seq_page_cost and random_page_cost相关参数配置
hdd硬盘:
seq_page_cost=1.0
random_page_cost=4.0
ssd硬盘:
seq_page_cost=1.0
random_page_cost=1.0
单表查询成本估算之排序
· sort
成本估算公式:

估算以下查询语句排序成本:
testdb=# select id, data from tbl where data < 240 order by id;
· sort成本估算

-->> 往期公开课资料,联系cuug客服领取
以上就是【postgresql从小白到专家】第29讲 -执行计划与成本估算 的内容,欢迎进群一起探讨交流
钉钉交流群:35822460,钉钉群专门有视频讲解